Under eIDAS 2.0, any organization or entity that aims to provide qualified trust services within the EEA must become a Qualified Trust Service Provider, or QTSP.
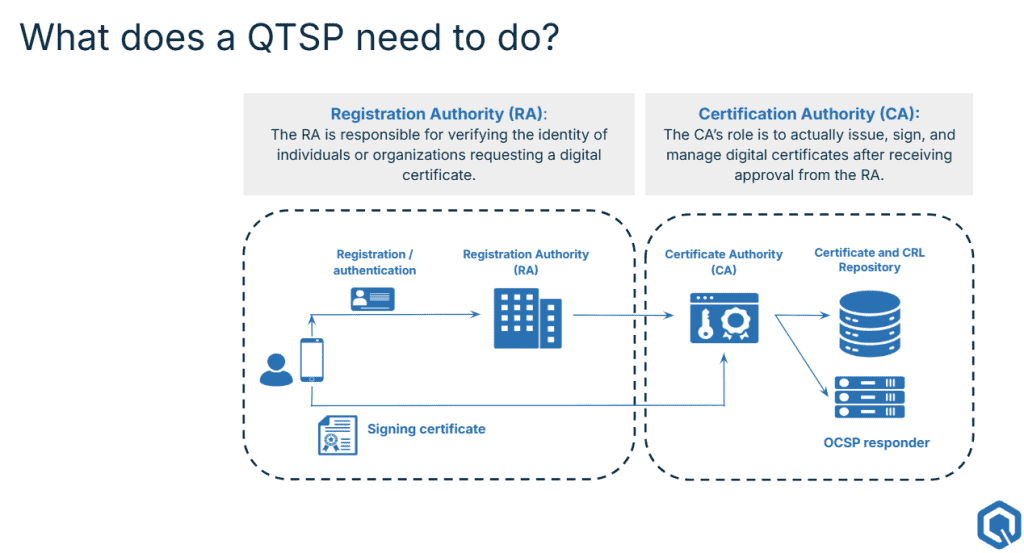
For organizations aiming to become a QTSP, understanding the roles of the Registration Authority, or RA, and Certification Authority, or CA, is crucial. These two functions work together to ensure the security, authenticity, and reliability of digital identities and certificates.
What’s a Registration Authority?
The Registration Authority is responsible for verifying the identity of individuals or organizations that request a digital certificate. The RA plays a crucial role in ensuring that only legitimate users obtain certificates. It does so by:
- collecting and verifying identity documentation to confirm the user’s legitimacy.
- ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory frameworks for trust services.
- approving or rejecting certificate requests before they are forwarded to the CA for issuance.
While the RA does not issue certificates, it serves as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only verified identities proceed to the next stage.
What’s a Certification Authority?
The Certification Authority is responsible for issuing, signing, and managing digital certificates. After receiving approval from the RA, the CA will:
- generate the digital certificate, binding the verified identity to a cryptographic key.
- digitally sign the certificate to guarantee its authenticity and prevent tampering.
- manage certificate revocation, ensuring that invalid or compromised certificates are promptly listed in Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or become accessible through the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP).
The CA acts as the backbone of digital trust, ensuring that issued certificates remain valid, secure, and traceable.
Why are the RA & CA essential for QTSPs?
Under eIDAS 2.0 and other regulations, QTSPs must follow strict security and compliance measures. The RA and CA partnership therefore ensures:
- Identity assurance: Only verified individuals or organizations receive certificates.
- Strong security: Digital certificates are issued under strict cryptographic controls.
- Trust and compliance: Certificates comply with regulatory requirements and remain valid throughout their lifecycle.
Building the foundation of a digital identity ecosystem
The RA and CA perform distinct but complementary functions within the QTSP framework. The RA ensures the legitimacy of certificate applicants, while the CA issues and manages certificates securely. Together, they form the foundation of a trustworthy digital identity ecosystem, essential for secure communications, transactions, and authentication in the digital world.