“The architecture reference framework from the EU recognizes that mobile phones or EU digital wallets on mobile phones need hardware back storage. They need a secure chip, like in a passport, to store your digital credentials securely for verifiers and issuers to have confidence in the authenticity of the identity claims.” This critical insight from Boris Goranov, CEO of Ubiqu, highlights one of the many technical challenges organizations face as they prepare for the implementation of eIDAS 2.0.
In this article, we’ll explore the key takeaways from a recent webinar featuring Steffen Schwalm, Principal Business Consultant at msg Group, and Boris Goranov, moderated by Jon Shamah, Director at Global Trust Foundation. We’ll delve into what it means to become a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP), the technological requirements for compliance, and strategic considerations for organizations navigating this complex regulatory landscape.
What is eIDAS 2.0 and why does it matter?
eIDAS 2.0 represents a significant update to the European regulation that has been in place since 2014. Published in May 2024, this regulation introduces several new trust services and mandates the creation of European Digital Identity (EUDI) wallets for citizens and companies across Europe.
“eIDAS 2.0 enables Europeans to maintain control of their own identities while establishing a framework of legal trust,” explained Steffen during the webinar. “A primary goal is to standardize electronic trust services across Europe, addressing the inconsistencies we experienced under eIDAS 1.” This standardization will have far-reaching implications for organizations handling digital identities and transactions throughout Europe.
Understanding qualified trust services
Qualified trust services form the backbone of digital trust under eIDAS 2.0. These services extend far beyond traditional identity verification to encompass the entire lifecycle of digital interactions.
As Steffen noted, “Qualified trust services encompass a comprehensive range of electronic services that establish legal validity across digital interactions.” The range includes issuing certificates for signatures and seals, timestamps, validation services, eDelivery for secure communication, and several new additions such as attestations of attributes, ledger services, and archiving services. This expansion dramatically increases the scope and potential use cases for QTSPs across various industries.
The path to becoming a QTSP
Becoming a Qualified Trust Service Provider requires a rigorous certification process overseen by conformity assessment bodies. This process ensures that QTSPs meet the high security and trust standards necessary for handling sensitive digital interactions.
“The path to QTSP status requires passing a comprehensive conformity assessment conducted by authorized bodies,” Steffen emphasized. This assessment evaluates an organization’s security measures, business continuity management, and implementation of specific standards related to the type of trust service being offered. The process includes document checks and on-site testing to verify that what has been documented has been properly implemented.
Learn more about how to become a QTSP.
Strategic considerations for organizations
When deciding whether to become a QTSP, organizations must carefully consider their business model, target market, and transaction volume.
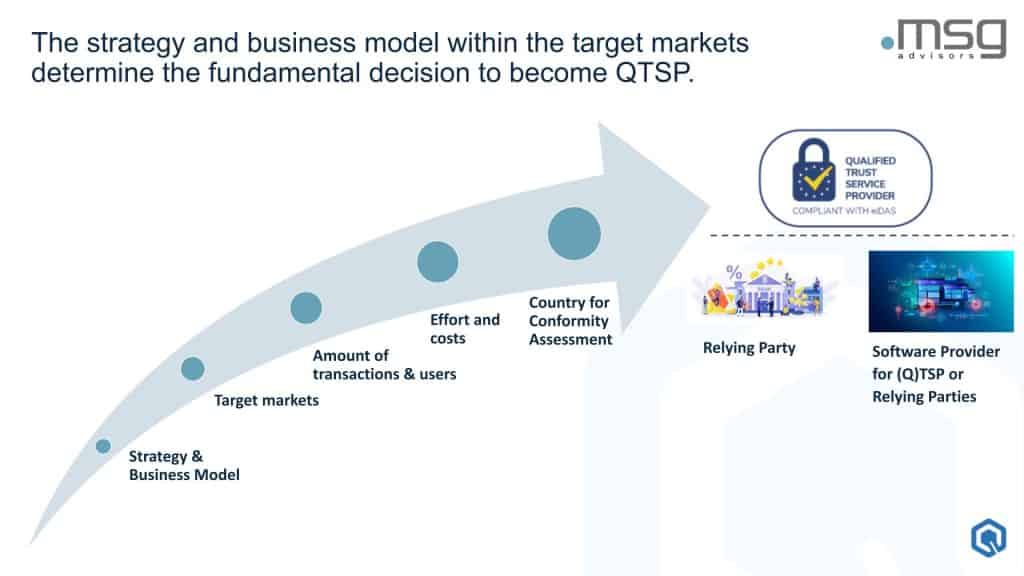
“Organizations issuing a relatively small volume of attestations—perhaps 100 per month—may find it more advantageous to partner with an existing QTSP rather than becoming one themselves,” advised Steffen. For organizations with higher volumes or those already operating identity platforms, becoming a QTSP themselves might be the more strategic choice. The decision should align with the organization’s broader goals and capabilities.
Technology options for EU digital identity wallets
The EU Architecture Reference Framework identifies four options for implementing the secure hardware elements required for digital identity wallets:
- Digital identity cards (physical cards used with mobile phones)
- Storage from device manufacturers (Apple, Google, Samsung)
- SIM cards from mobile network operators
- Remote secure elements (hardware in data centers connected to mobile phones)
“When evaluating these solutions, eIDAS High compliance is the primary requirement to ensure proper security,” explained Boris. Currently, only digital ID cards and remote secure elements fully meet compliance requirements, while the other options face significant challenges, like we explain in this article: “The 4 main Wallet Secure Cryptographic Devices (WSCD)”.
Implementation approaches for becoming a QTSP
Organizations looking to become QTSPs have three main approaches: outsourcing to an existing QTSP, building everything in-house, or adopting a hybrid approach that leverages pre-certified components.
Boris outlined the challenges with the fully in-house approach: “Building a complete QTSP infrastructure in-house provides control over all processes and technologies, but typically requires two to three years to achieve certification.” For many organizations, the hybrid approach offers an attractive middle ground, allowing them to maintain control while accelerating their time to market by using pre-certified technological components.
The business opportunities of attestation of attributes
One of the most exciting aspects of eIDAS 2.0 is the virtually unlimited potential for attestation of attributes across different sectors and use cases.
“The applications for attestation of attributes are practically limitless,” emphasized Steffen. “Industries can implement these for supply chain verification, maintenance documentation for aircraft and machinery, secure data sharing, and numerous other use cases.” This flexibility opens doors to innovative applications in healthcare, finance, transportation, and numerous other fields.
Preparing for the 2026 deadline
With eIDAS 2.0 enacted, organizations have until December 2026 to ensure their systems and processes are compliant. This timeline means that strategic decisions and implementation planning should be happening now.
“With the eIDAS regulation now enacted, we have 19 months remaining until the December 2026 deadline to implement compliant wallets and authentic sources,” Boris reminded the audience. This deadline applies to both wallet providers and the authentic sources that will issue credentials into those wallets. Organizations need to develop a clear roadmap for compliance, considering both the technological and organizational aspects of their implementation strategy.
Conclusion
As eIDAS 2.0 reshapes Europe’s digital identity landscape, organizations face challenges and opportunities. Those who strategically approach QTSP certification and wallet implementation will be well-positioned to thrive in this new environment.
The insights Steffen Schwalm and Boris Goranov provided during the webinar highlight the importance of making informed decisions about technology, certification approach, and market strategy. Whether an organization chooses to become a QTSP itself or leverage the services of existing providers, understanding the regulatory requirements and technological options is essential for success under eIDAS 2.0.
Ubiqu offers innovative solutions that address the complex security challenges of eIDAS 2.0 compliance. Our Remote Secure Element technology provides organizations with a powerful, compliant foundation for digital identity wallets while dramatically reducing implementation time and complexity. Whether you’re becoming a QTSP or implementing an EU digital identity wallet, Ubiqu’s pre-certified components can help you accelerate your path to compliance while maintaining full control of your digital identity strategy.


